Click here and press the right key for the next slide (or swipe left)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts
Syntax
What features are characteristic of language?
S’s 13:11 utterance of ‘Earth is being warmed by human activity’ is true exactly if Earth is being warmed by human activity.
S’s 13:11 utterance of ‘Mars is being warmed by human activity’ is true exactly if Mars is being warmed by human activity.
‘A semantic theory for a particular natural language will … articulate an assignment of meanings to sentences …
It will also display just how the sentences come to have the meanings they do, given their construction out of more basic constituents: it will reveal semantic structure. …
The recurrent contribution that a constituent expression makes to the meanings of several sentences in which it occurs will be revealed in the use of … the principle assigning a semantic property to that expression … in the derivations of meaning assignments for all those sentences”
(Davies 1986: 130).
How is constructing a semantic theory possible?
obstacle: there are uncountably many sentences.
[Compositionality]
The meaning of a sentence (and of any complex expression) is fully determined by its structure and the meanings of its constituent words.
Semantics requires syntax.
Contrast to be explained:
‘Music makes swans purple above’ is an English sentence.
‘Water swans in swim’ is not an English sentence.
What does a syntact theory reveal?

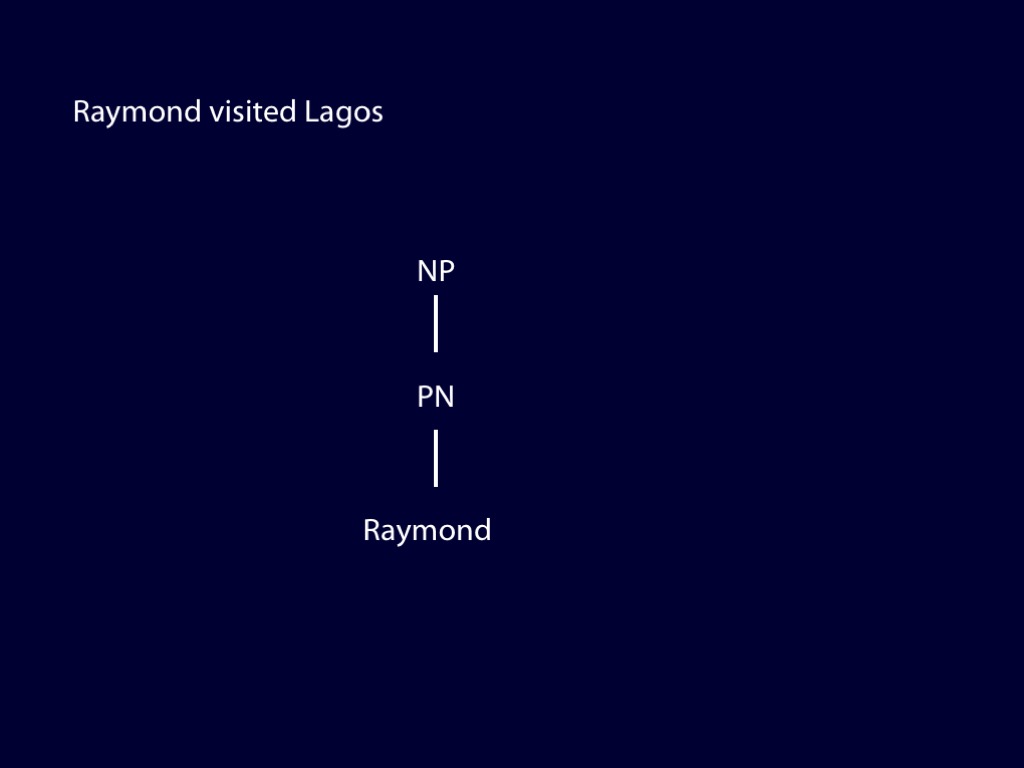
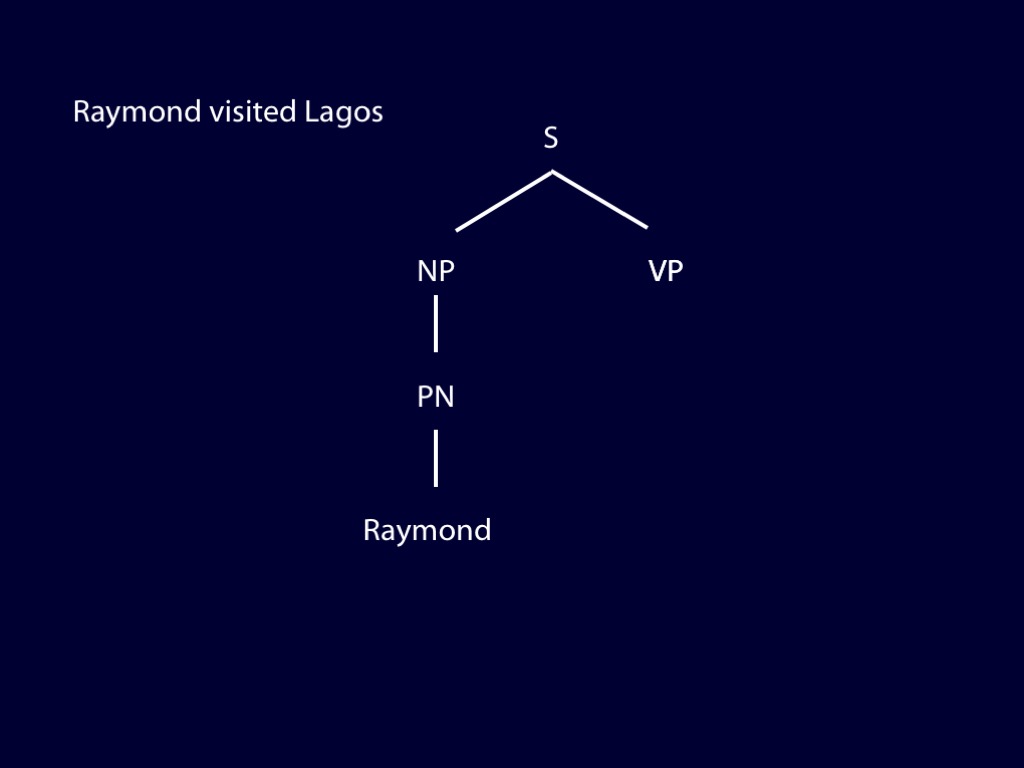
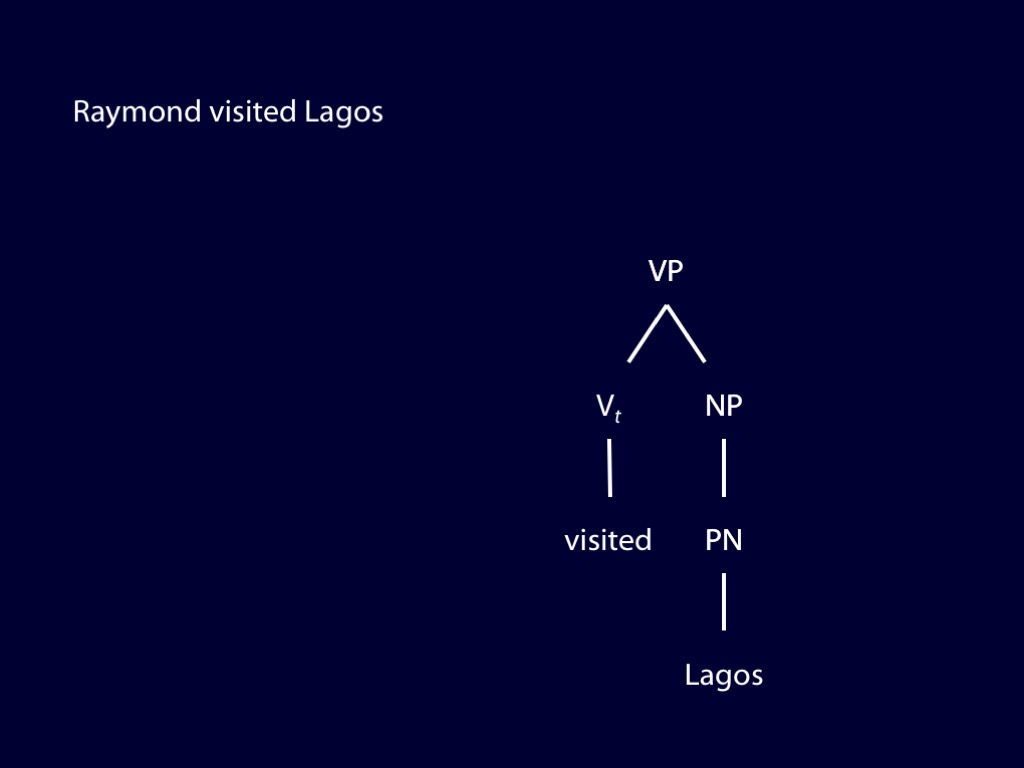
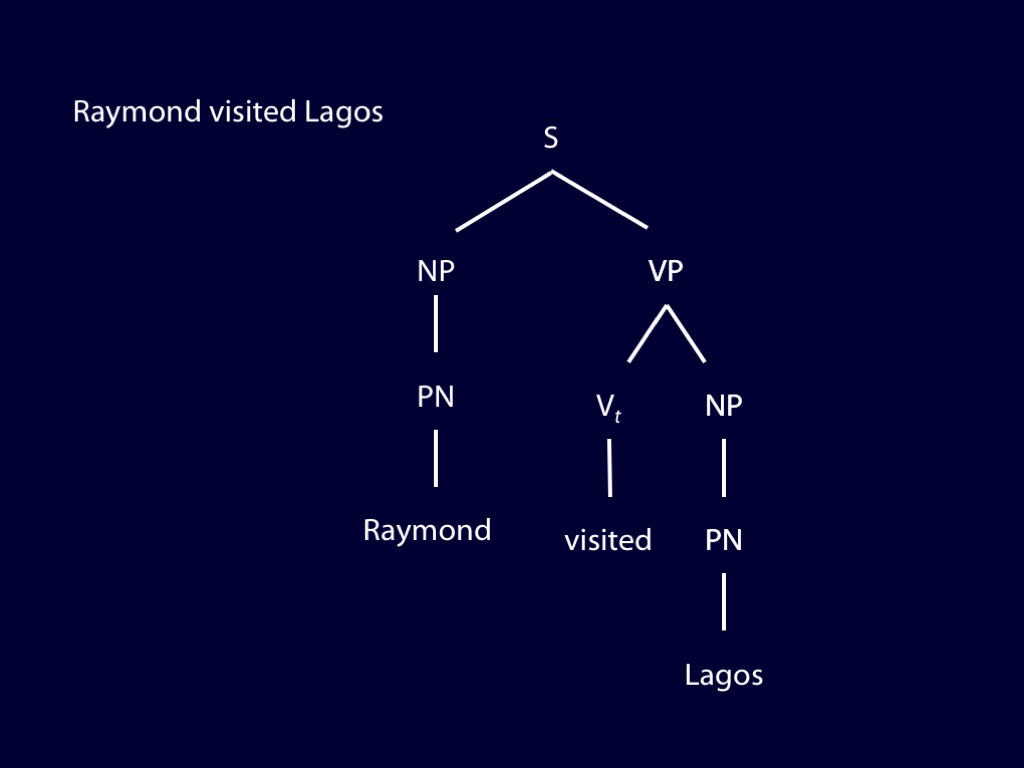
How can we discover the syntactic structure of a sentence you utter?
the red ball
‘I’ll play with this red ball and you can play with that one.’
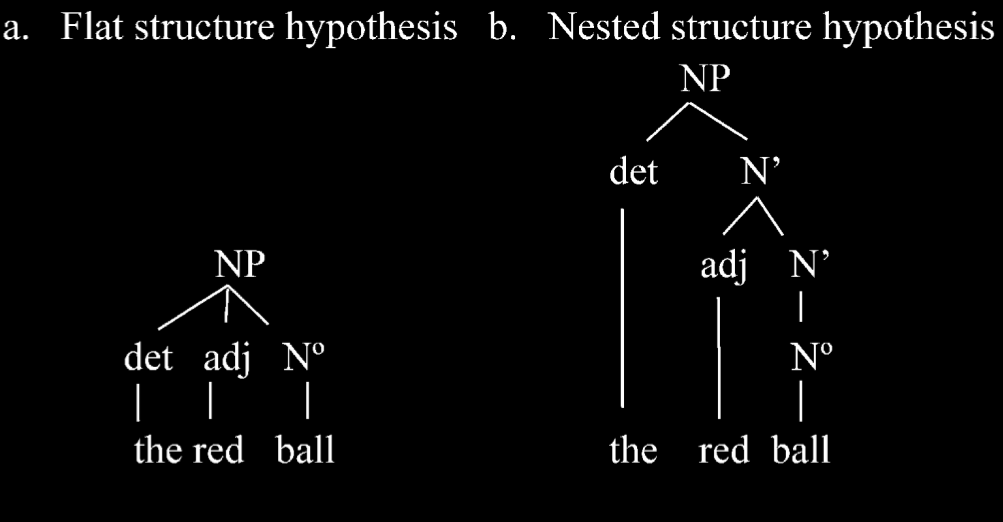
Lidz et al (2003)
- \item ‘red ball’ is a constituent on (b) but not on (a)
- \item anaphoric pronouns can only refer to constituents
- \item In the sentence ‘I’ll play with this red ball and you can play with that one.’, the word ‘one’ is an anaphoric prononun that refers to ‘red ball’ (not just ball). \citep{lidz:2003_what,lidz:2004_reaffirming}.
How can we discover the syntactic structure of a sentence you utter?
Two Questions
What are the syntactic structures of those sentences?
What is the relation between these structures and those who utter them?
How is constructing a semantic theory possible?
obstacle: there are uncountably many sentences.
[Compositionality]
The meaning of a sentence (and of any complex expression) is fully determined by its structure and the meanings of its constituent words.
Summary
- The aim of semantics is to explain productivity and systematicity of language.
- We need semantics (not just syntax and pragmatics) in explaining how communication by language succeeds because languages are productive and systematic.
- Semantic theories attempt to explain systematicity and productivity by identifying compositional structure in languages.
- Success depends on discovering syntactic structures.
- Identifying compositional structure requires assigning semantic values to fragments of sentences; part of this is provided by the theory of reference.